Restructuring an electricity sector entails a complex realignment of political and economic institutions, which may both delay and distort the achievement of satisfactorily competitive conditions. In research and planning for policy interventions in power systems under these varied regulatory environments, typical operational models may neglect important interactions between techno-economic criteria and political constraints, leading to poor understanding of underlying causes of inefficiency and to inappropriate recommendations. We develop tractable formulations of the unit commitment problem based on integer clustering of similar units that endogenize important political factors in the Northeast grid region of China. We demonstrate the importance of these interactions on operations and provide a set of options for researchers to explore further pathways for China’s ongoing power system reforms. For example, wind integration, a key policy priority, is inhibited by the interaction of institutions limiting short- and long-term sources of flexibilities in inter-provincial trade.
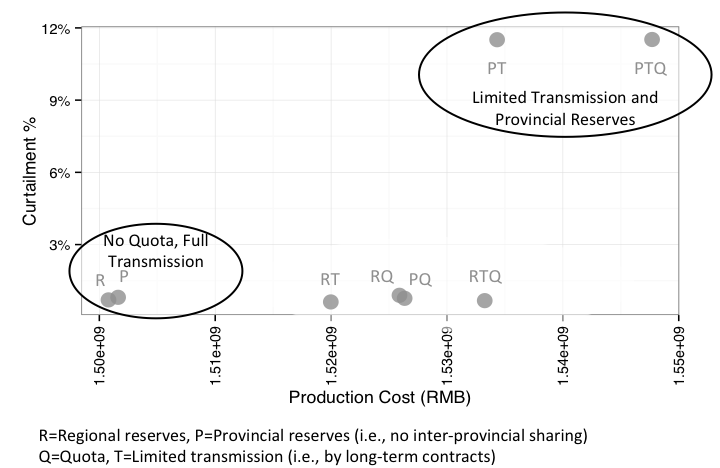 Figure - Modeled cost and wind curtailment under different institutional combinations
Figure - Modeled cost and wind curtailment under different institutional combinations
Recommended citation:
Davidson, M. R., Pérez-Arriaga, J. I. (2017). Modeling Unit Commitment in Political Context: Case of China’s Partially Restructured Electricity Sector. MIT CEEPR Working Paper.
